Since greenhouse conditions allow rapid development of pest populations, early detection and diagnosis of pest insects are necessary to make control decisions before the problem gets out of hand and you suffer economic loss.
Some common and important greenhouse arthropod pests to keep a close watch for are: aphids, fungus gnats, thrips, whiteflies, root aphids and mites. The most frequently observed diseases are: powdery mildew, botrytis, pythium and fusarium. Below is a description of each pest and corresponding symptoms to look for.
Aphids
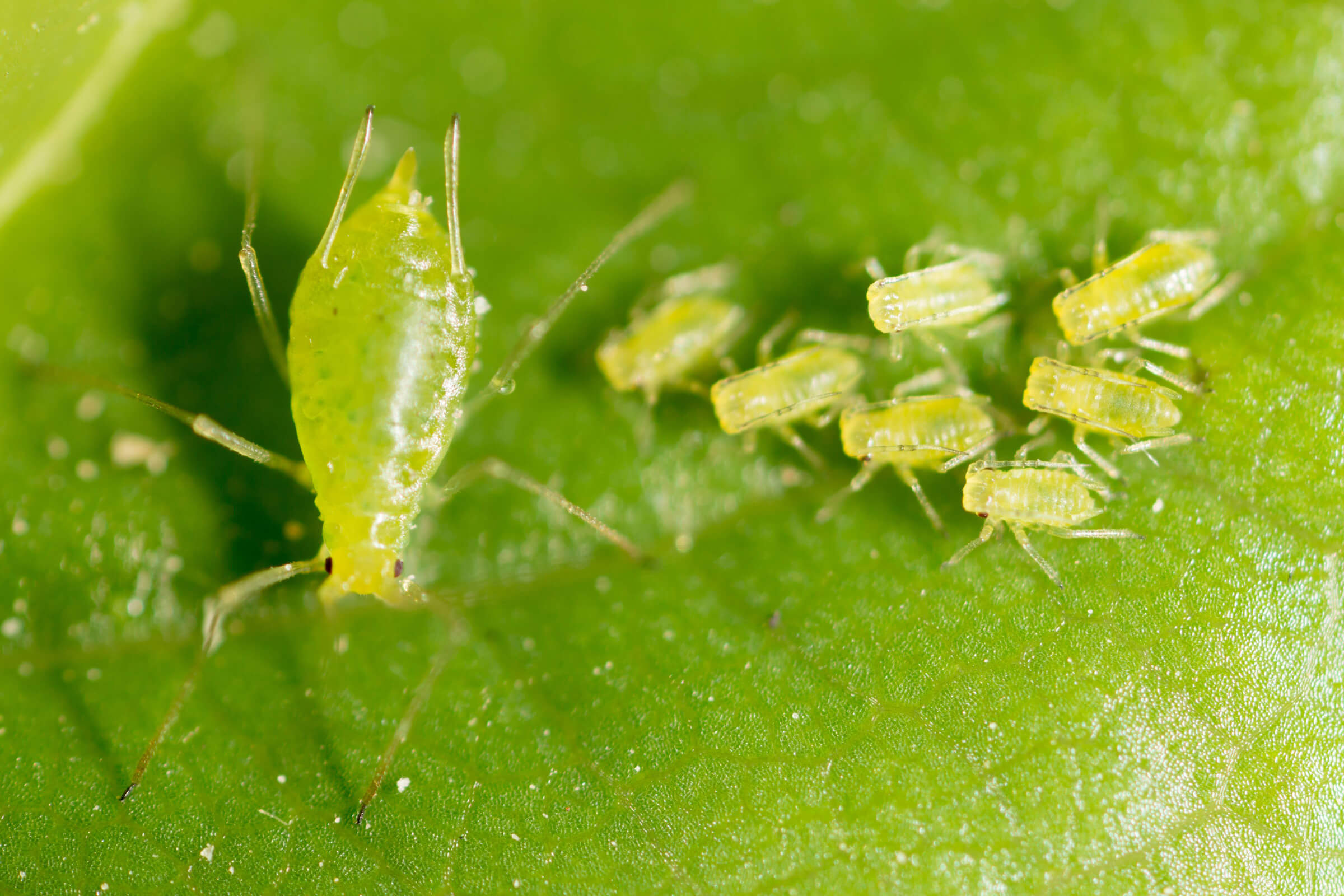
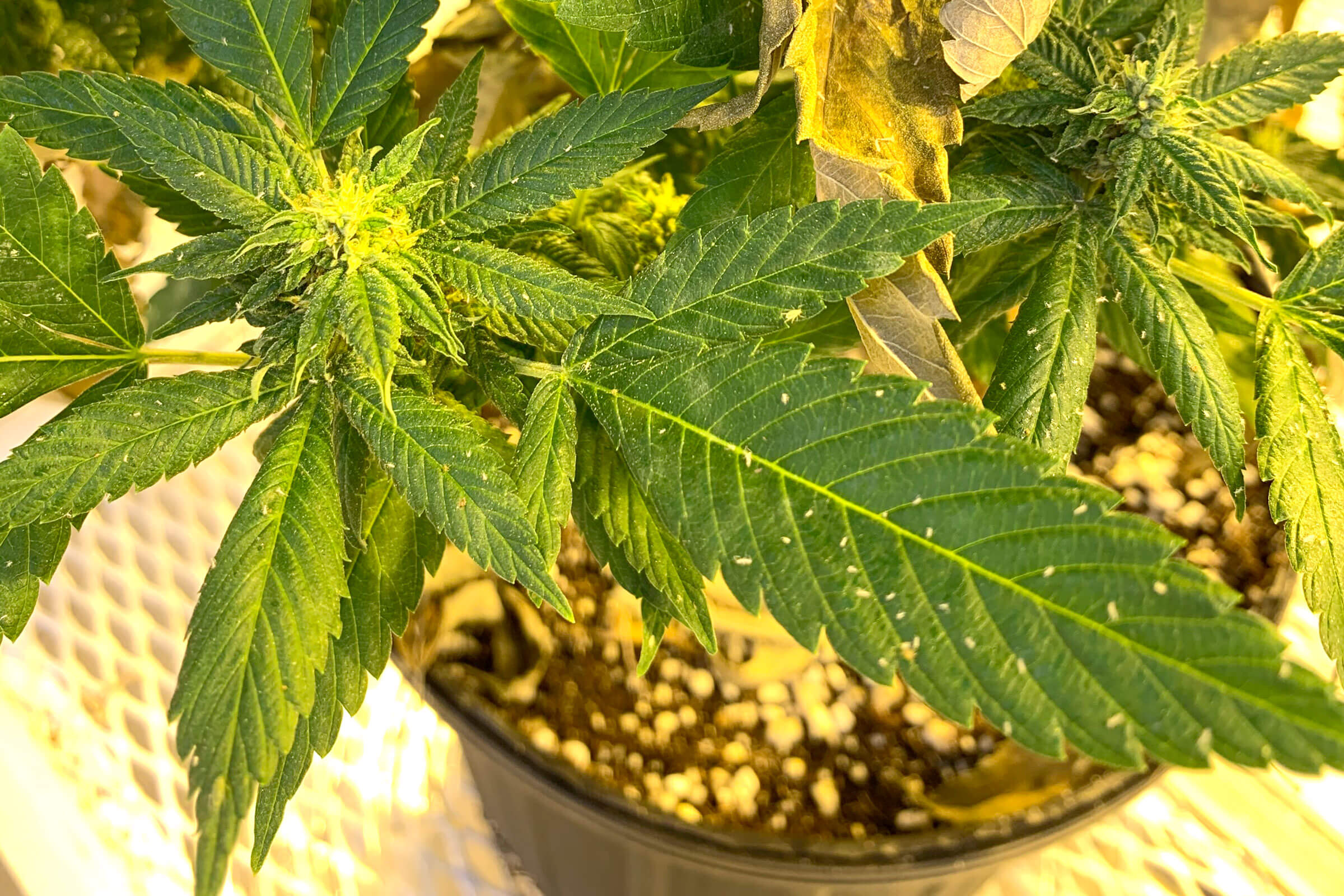
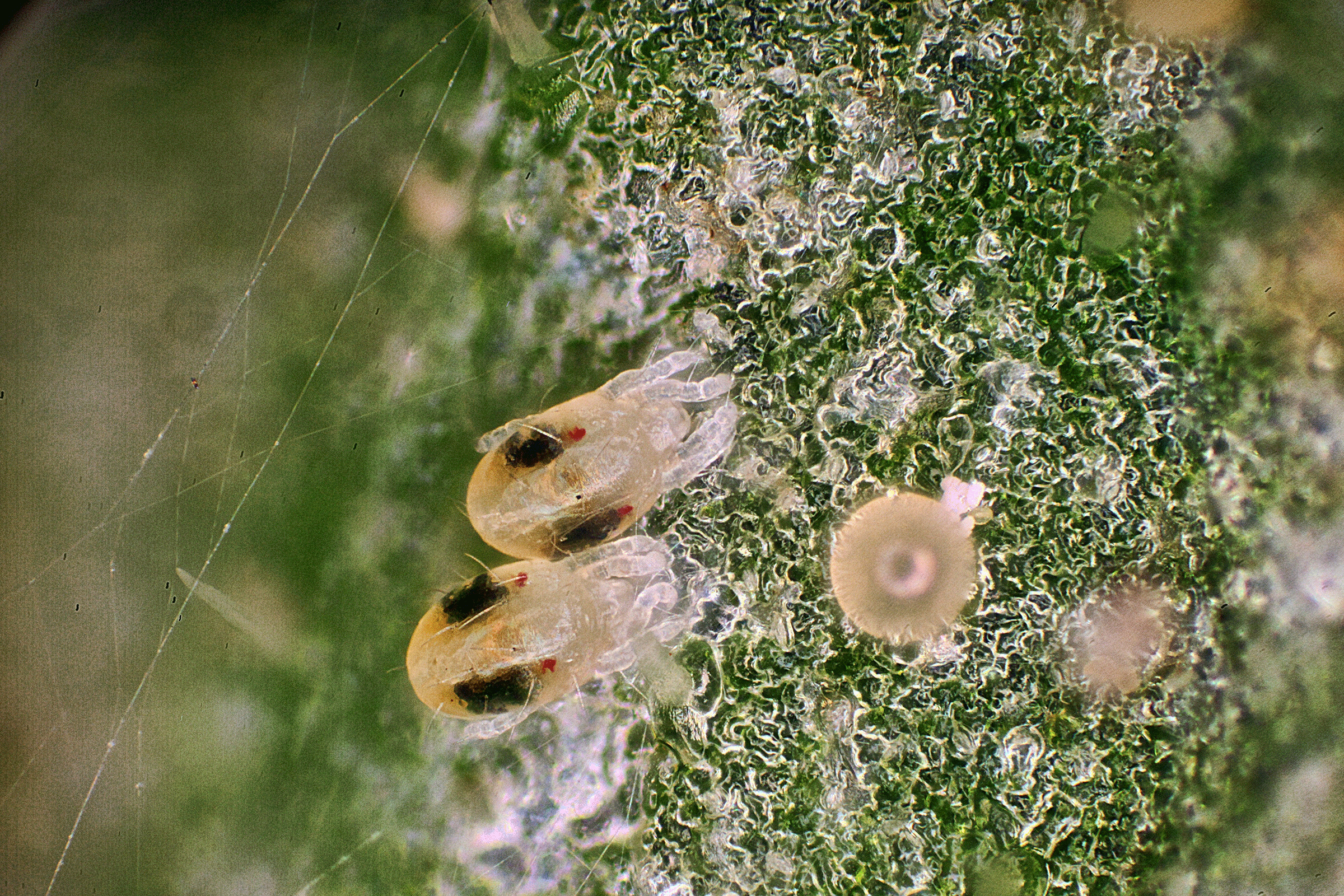
Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) are a typical insect pest of greenhouses which feed on a wide variety of plants by piercing leaf cells and sucking out their contents by means of their stylets. Aphids are commonly small (3 mm – 5 mm in length), most have a pear-shaped body and may or may not have wings. Winged individuals increase when there is the need to leave the plant due to overcrowding or a decline in food quality.
Aphids are also known for vectoring plant viruses and releasing relatively large amounts of honeydew waste product, which is fairly visible on plant leaves as translucent, wet spots, which feel sticky when touched. Aphids usually occur in colonies located mainly on the undersides of leaves, on stems or clustered nearby buds. If a Hemp plant becomes heavily infested, its leaves can turn yellow and/or wilt due to the excessive stress and leaf damage. Presence of translucent honeydew spots also can be found, as well as white skin residue left behind by nymphs. Development of fungal diseases can also occur in correspondence to honeydew accumulation spots.
Thrips
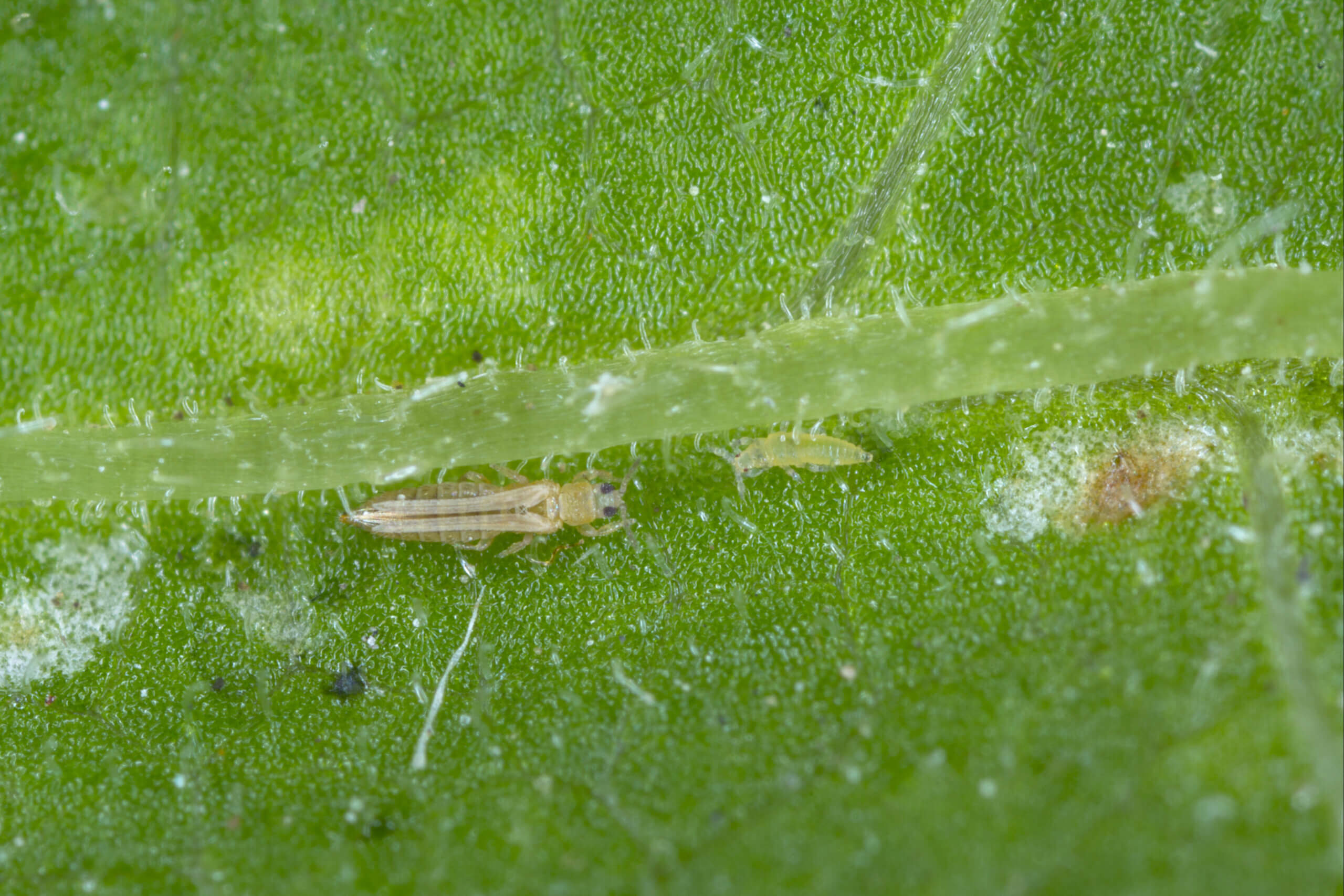
Thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) are a severe insect pest of greenhouses which feed on a wide variety of plants by piercing surface cells of leaves and sucking out the cell contents by means of their stylets. Thrips are also known for vectoring plant tospoviruses such as the impatiens necrotic spot and tomato spotted wilt virus. Females have a high reproductive capacity, a rapid life cycle which allows for multiple generations per year, and tend to reside in cryptic habitats such as unopened terminals, making control practices difficult. Thrips are minute, slender-bodied insects (1 mm – 1.2 mm long) with four narrow wings folded flat over the back and fringed with hair.
Toward the end of the second larval stage, the thrips stop feeding and drop or enter the soil or leaf litter. Winged adults then emerge from the pupal stage in 1 to 3 days, depending upon temperature. Thrips like to feed on buds and new leaves, where they pierce plant cells with their mouthparts and suck out their contents, but they can also be found at the bottom of the plant. Contrary to spider mites, thrips tend to feed more often on the upper leaf surface of plants. Bronze or silvery leaf scars and tiny black spots of fecal excrements are evident on leaves with heavy-feeding injury.
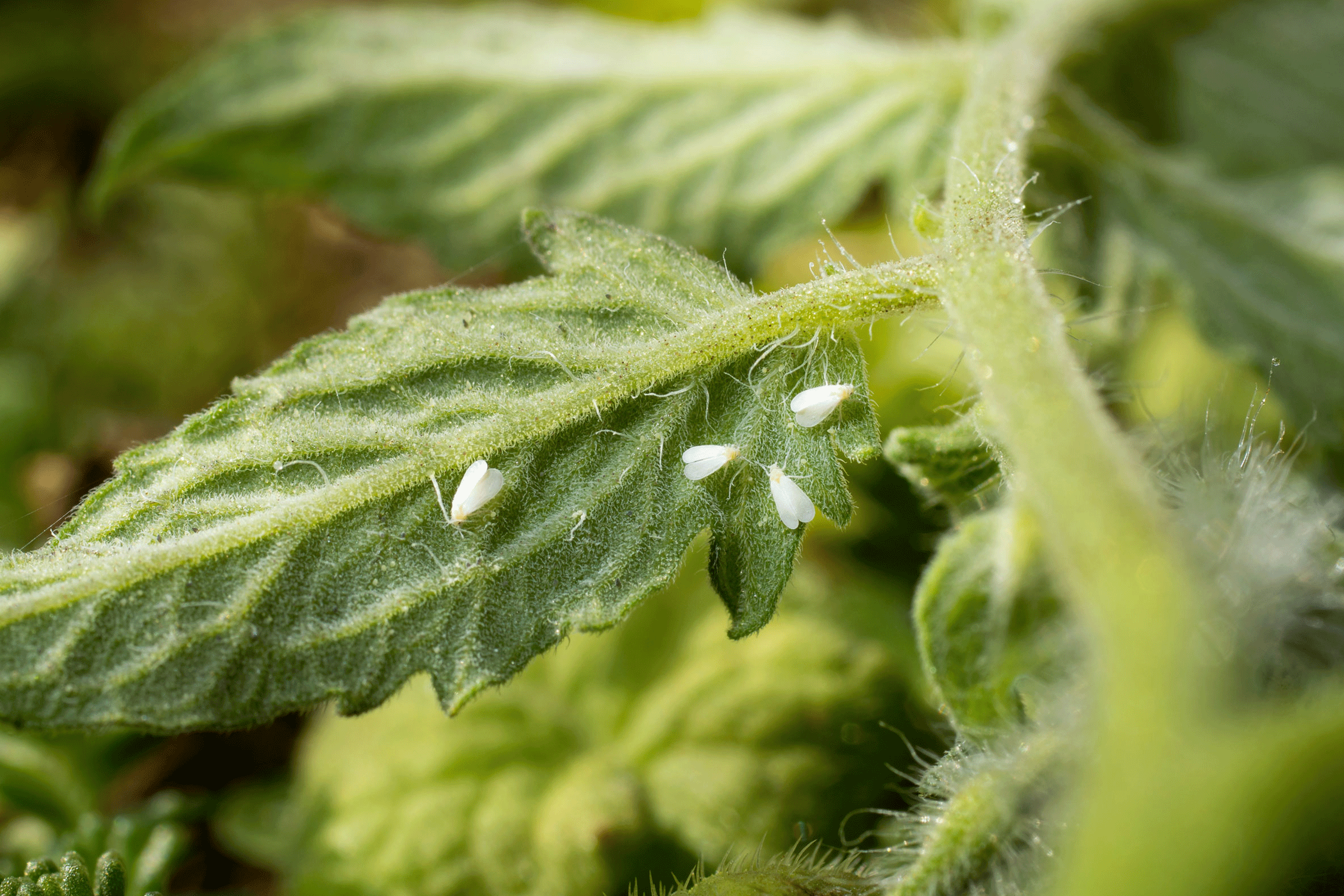
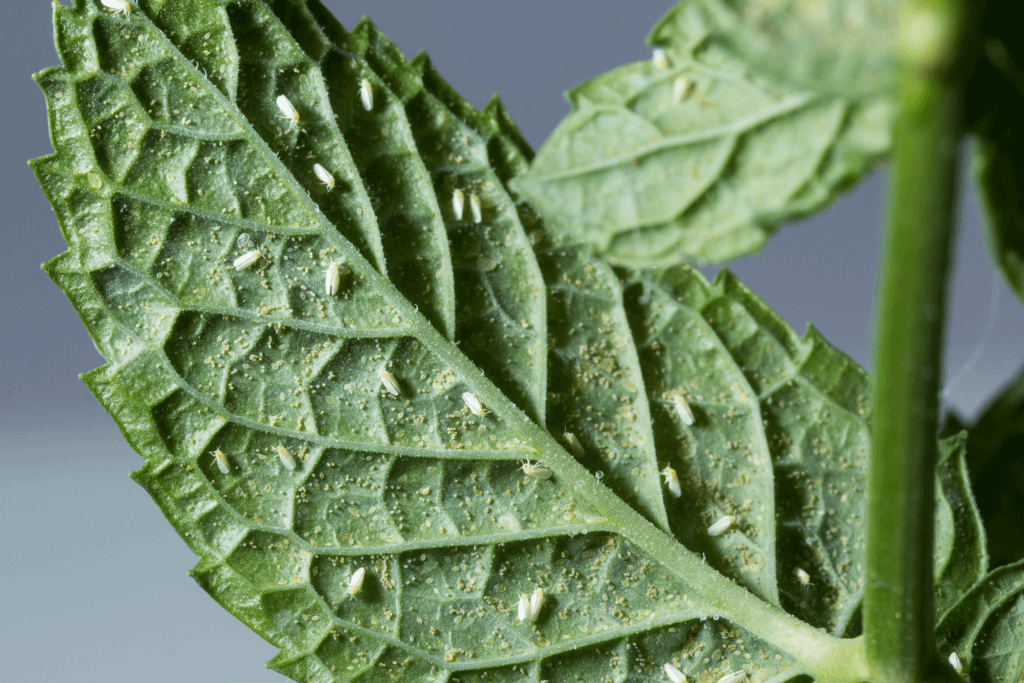
Whiteflies
Whiteflies (Diptera: Aleyrodidae) are white, soft-bodied, winged insects with a triangular shape, and are often found in clusters on the undersides of leaves. Whiteflies use their piercing, needlelike mouthparts to suck sap from phloem, the food-conducting tissues in plant stems and leaves. Large populations can cause leaves to turn yellow, appear dry, or fall off plants. Like aphids, whiteflies excrete a sugary liquid called honeydew, so leaves may be sticky or covered with black sooty mold that grows on honeydew.
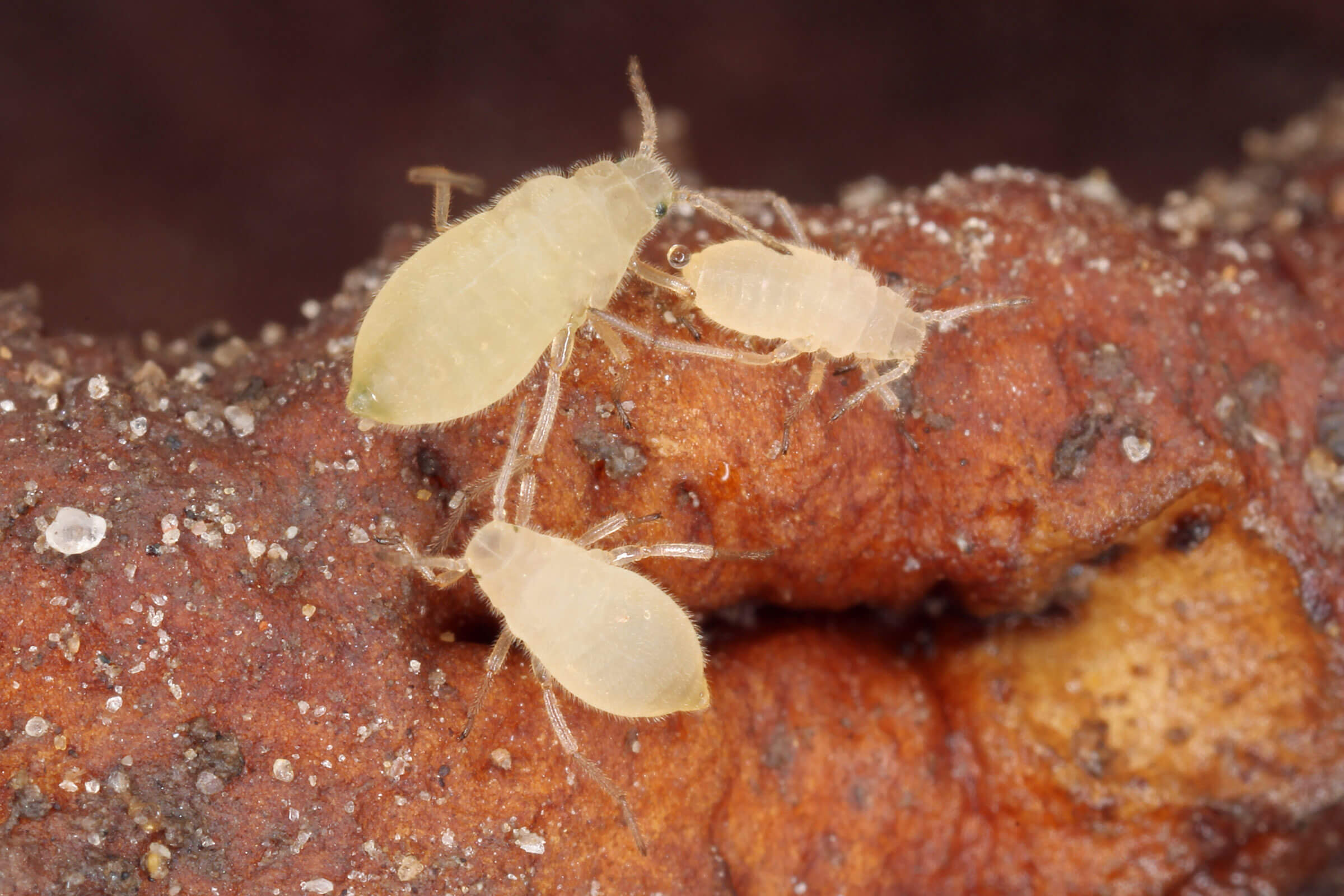
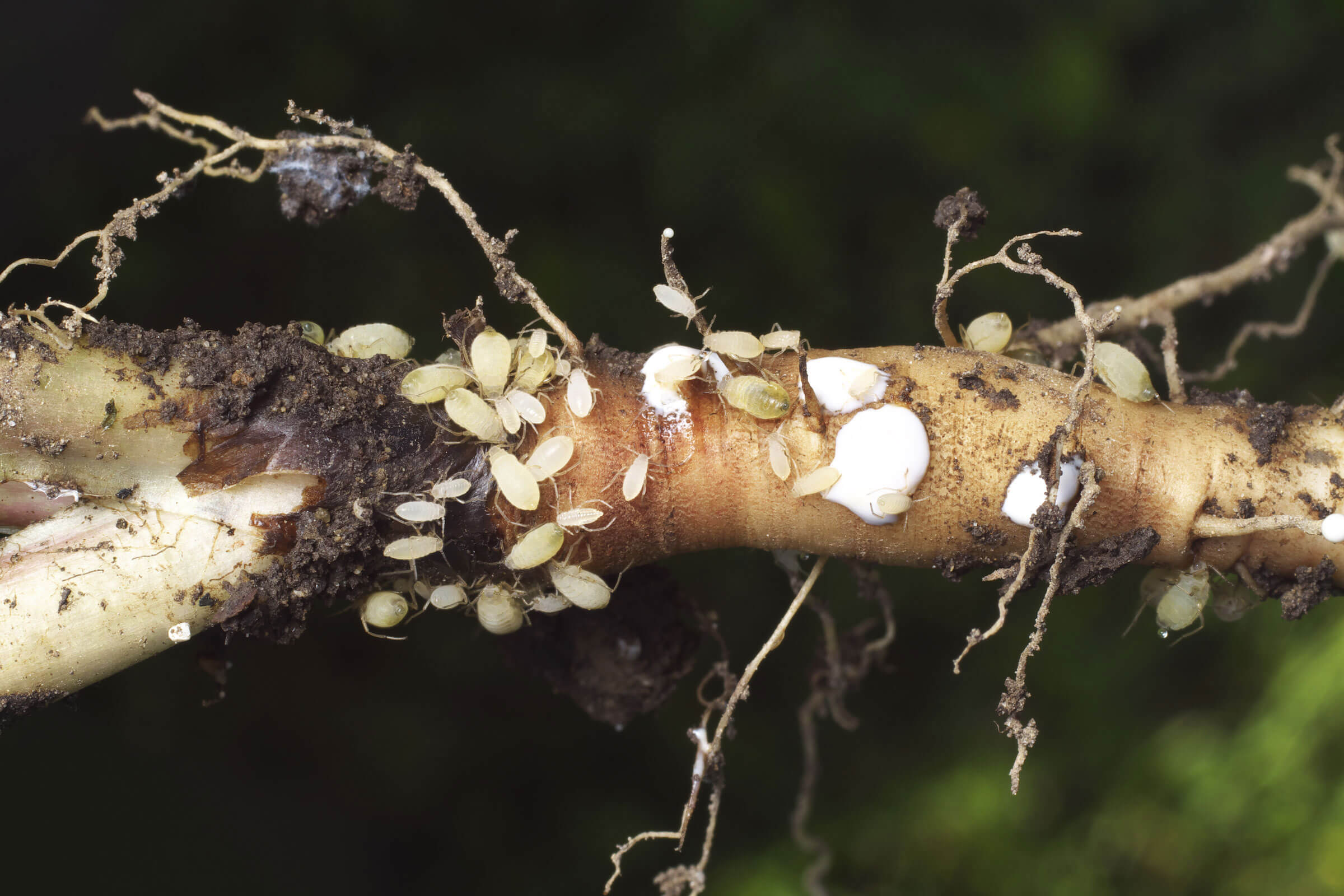
Root Aphids
They can produce a white, waxy secretion that covers their body and some is left behind as they move through the growing medium. This is often mistaken for mealybugs that are also covered with a white waxy or threadlike substance. It is best to use a hand lens and observe the roots to see the actual insect.
Minor infections of root aphids do not cause significant plant damage, however, as the populations increase, wounds in plant roots can become entry points for root disease pathogens. Plant roots cannot take up nutrients and therefore can exhibit nutrient deficiencies in the leaves. Plants often have a lack of vigor, are smaller and can wilt, especially during the heat of the day. Root aphids do not travel rapidly, so infections are often restricted to a few plants and spread slowly initially.
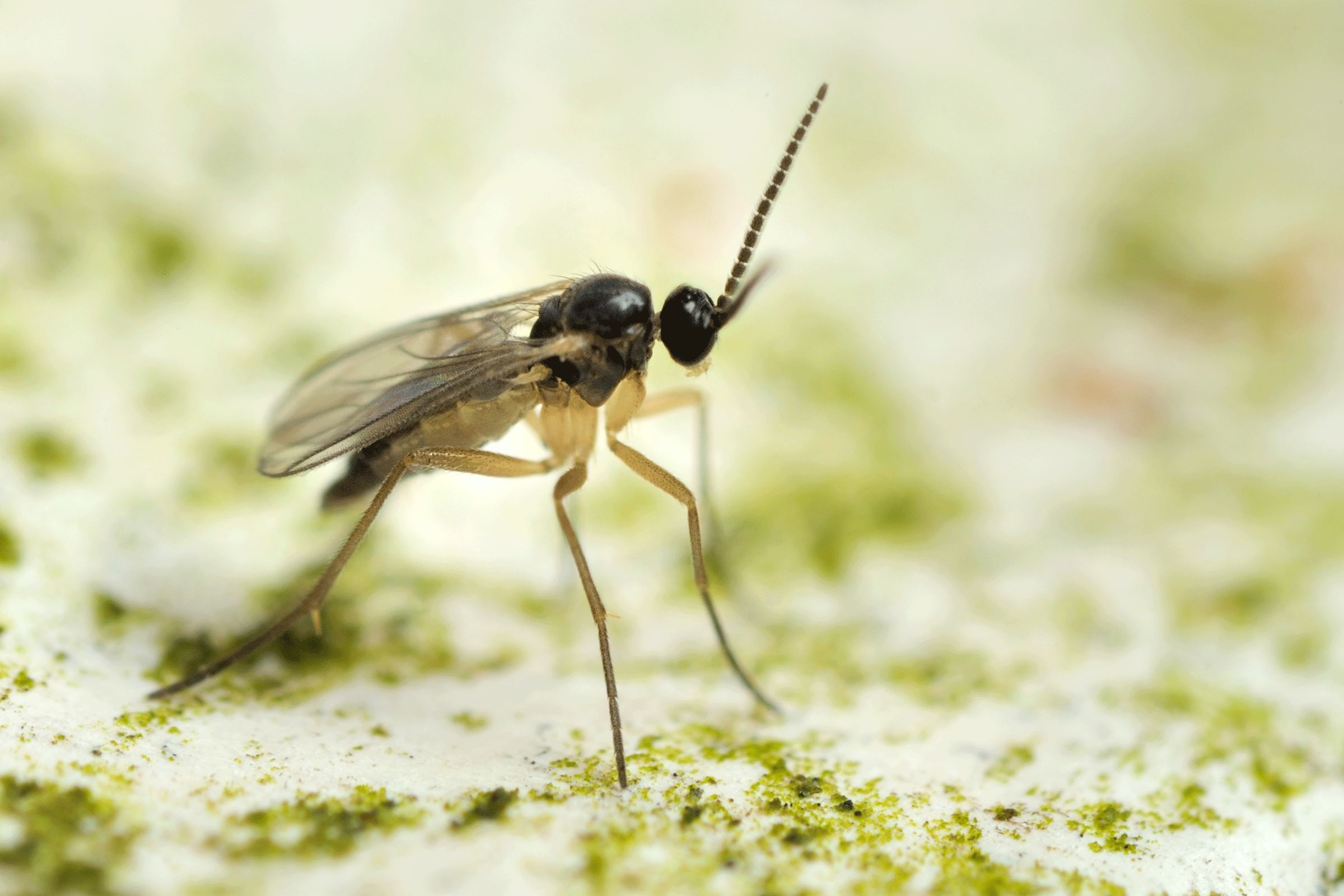
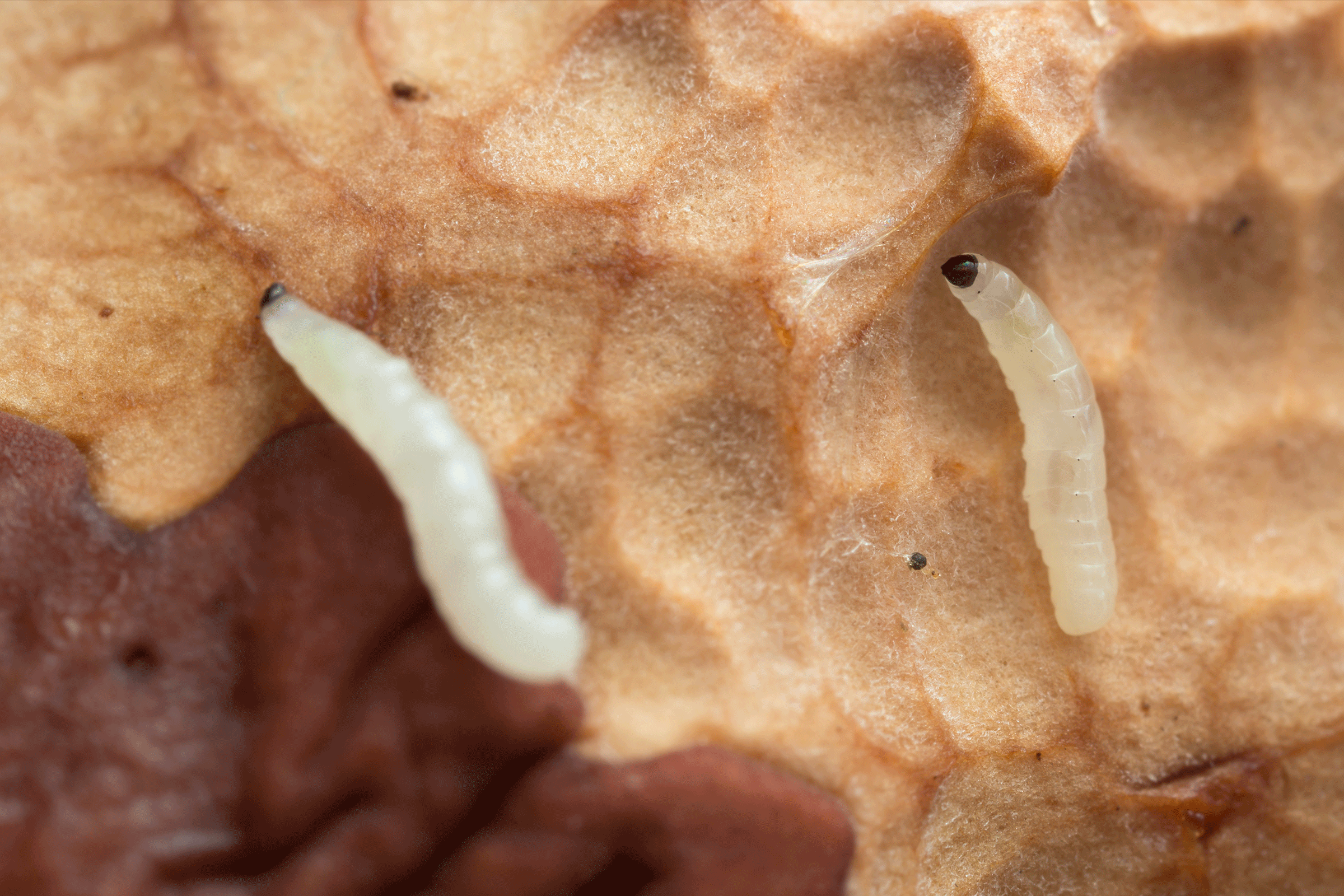
Fungus Gnats
The larvae are wormlike and translucent, with a black head capsule. Larvae usually are located in the top 2 to 3 inches of the growing medium, depending on moisture level. Larvae develop rapidly and are fully grown in two to three weeks. Moist growing media containing high amounts of peat moss are particularly attractive to adult females. Plants infested by numerous fungus gnat larvae can have stunted growth. The best way to determine if you have a fungus gnat infestation is by using sticky card traps and monitoring the number of captured adult individuals.
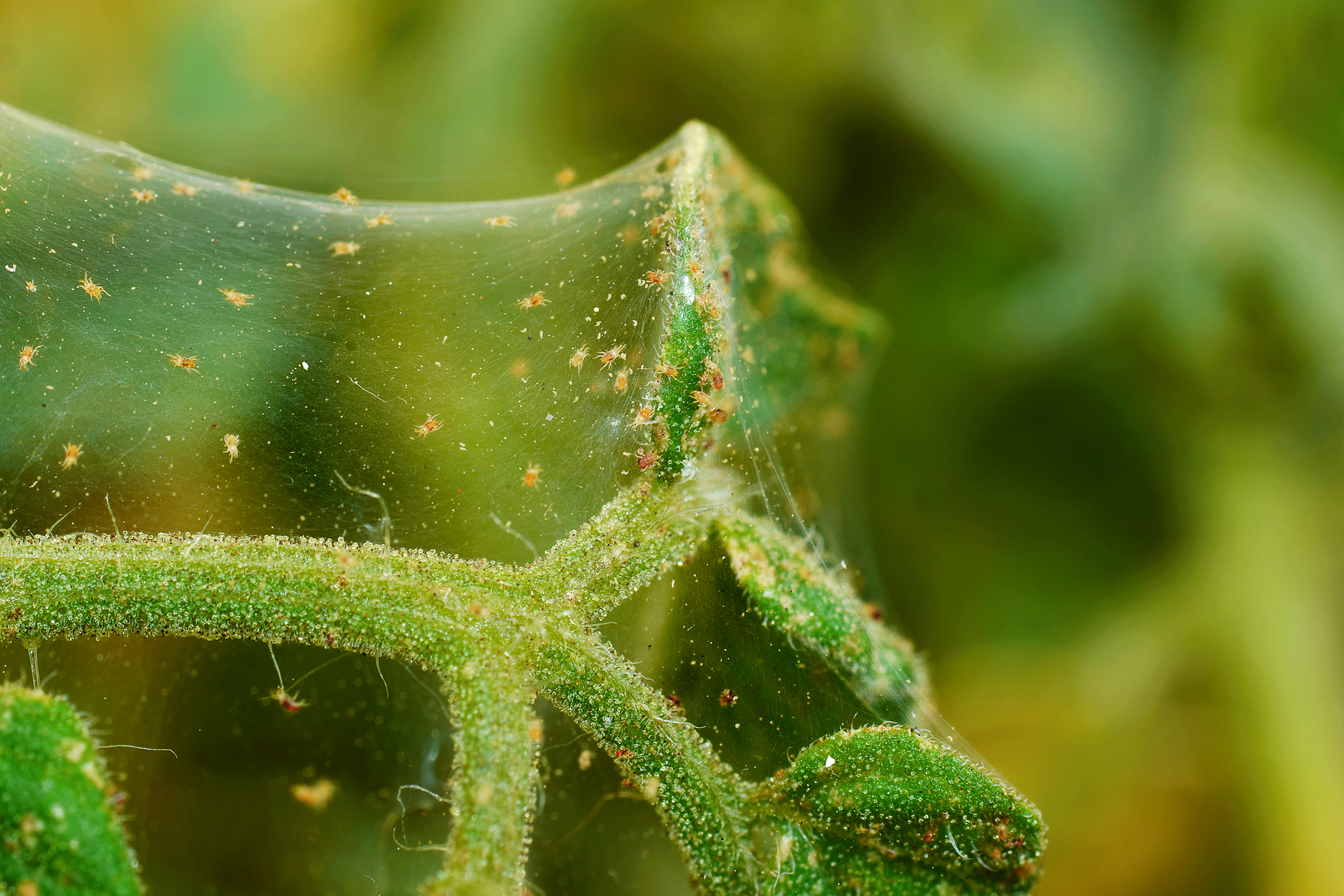
Spider Mites
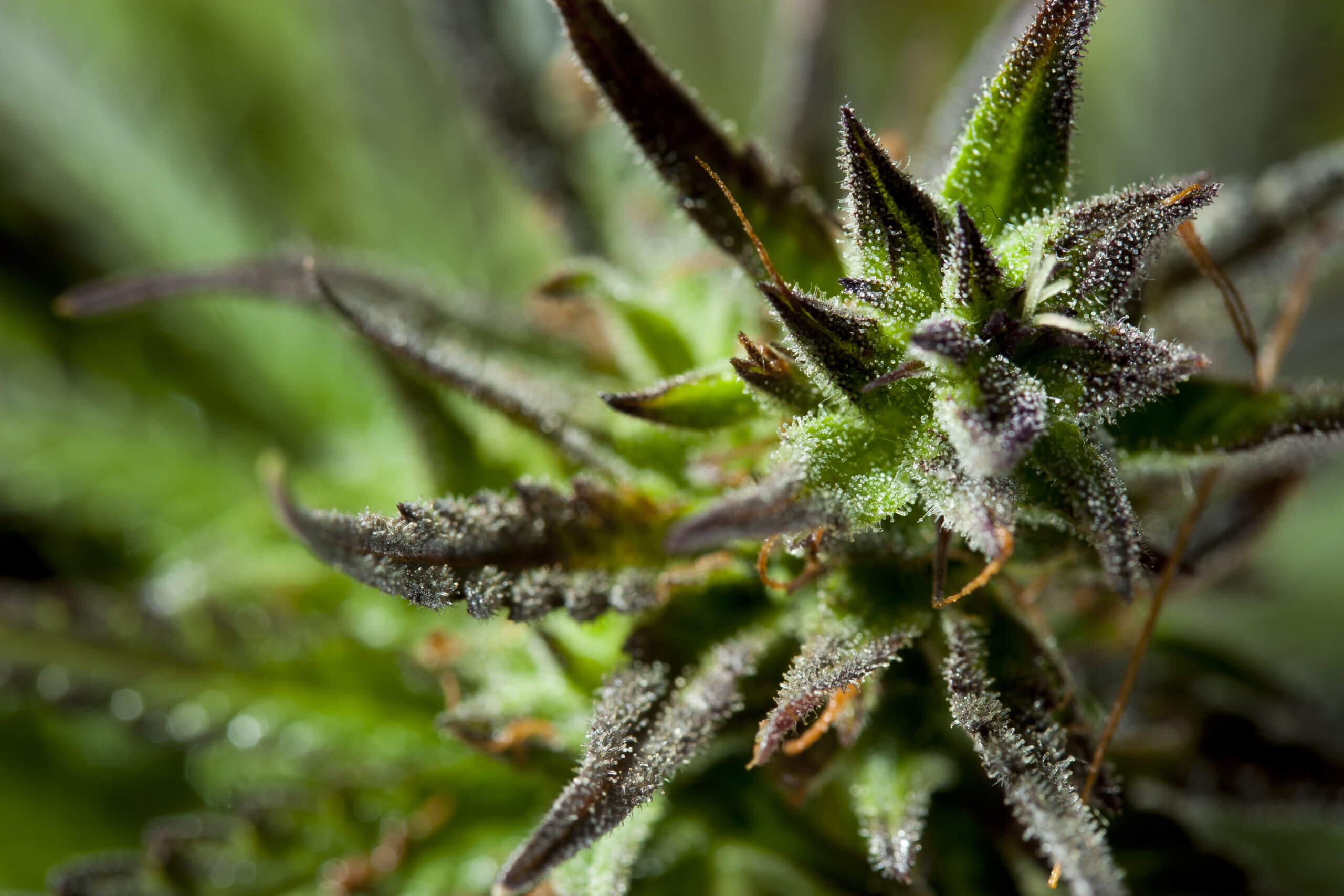
Spider mites (Acari:Tetranychidae) such as the two-spotted spider mite (Tetranichus urticae) are arthropods that feed on a variety of plant species by sucking the plant cell content through a pair of sharp stylets. Spider mites are tiny (approximately 0.5 mm in length) arachnids with 8 legs and a cream color appearance.
Populations can develop exponentially in a very short period of time. Eggs are laid in clusters on the underside of leaves. The initial stage of colonization commonly starts from the bottom third of the plant. Injury initially appears as stippling or yellowish-reddish brown spots on the leaves which are located in correspondence of the colony clusters typically found on the underside of the leaf. Leaves initially turn yellow and, with high population density, desiccate and die. On mature plants, branches above the main canopy and directly under growing lights are more likely to become infested with spider mites.
Hemp Russet Mites
HRM (Acari: Eriophyidae) is a specialist pest of Hemp and it feeds primarily on petioles and leaflets. HRM specifically feed on the surface layer of plant cells, piercing them with their minute mouthparts and feeding on the cell fluids. HRM have a very different appearance than spider mites; they do not produce webbing nor are visible with a naked eye. HRM are soft-bodied, sausage-shaped, exceptionally tiny, with two pairs of legs and no wings.
Contrary to spider mites, which can be seen with the naked eye, HRM require a higher level of magnification to be visible (15-20x). In enclosed areas, fans or even splashing water can quickly spread mites. No visible symptoms are produced when HRM are in low populations, but a range of subtle symptoms develop during outbreaks. Leaflets generally curl at the edges and may have a glossy wet look similar to heat stress. Leaves may have yellow or bronze spotting. Petioles become brittle and leaflets break off easily. In bad infestations, the mites crowd plants by the thousands and give leaflets a beige appearance. HRM also infests flowering tops.
Broad Mites (BM)
BM (Acari: Tarsonemidae) are an important pest of a wide variety of plants, including CBD Hemp. The mite commonly attacks young, growing plant parts and, similar to HRM, is very difficult to detect. They are colorless at first but become a rich amber when fully developed. Dispersal occurs through crawling, air currents and water.
BM are often found on young leaves and feed mostly on the under-surface of leaves. Infested plants become unthrifty. Leaves curl downward due to the mite’s saliva being toxic to plants, and take on a glossy, almost plastic-like appearance. Eventually affected leaves turn yellow or bronze and die. Internodes shorten and lateral buds break more than normal. This new growth may also be stunted or killed, which forces out additional shoots. Sometimes the symptoms can be confused for tobacco mosaic virus. Similar to HRM, leaf symptoms from BM are also commonly misdiagnosed as overwatering, a nutrient deficiency or heat damage.
Powdery Mildew
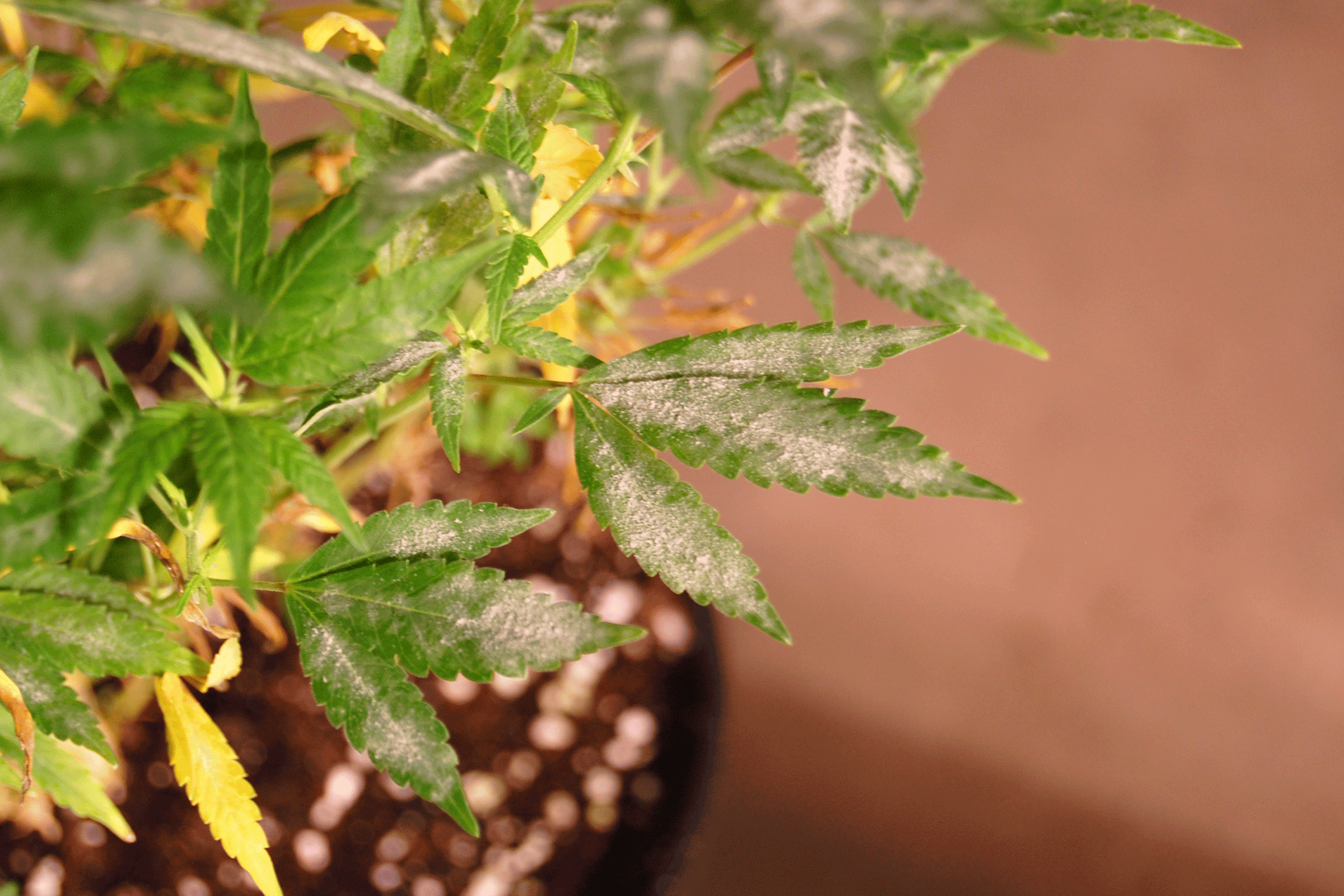
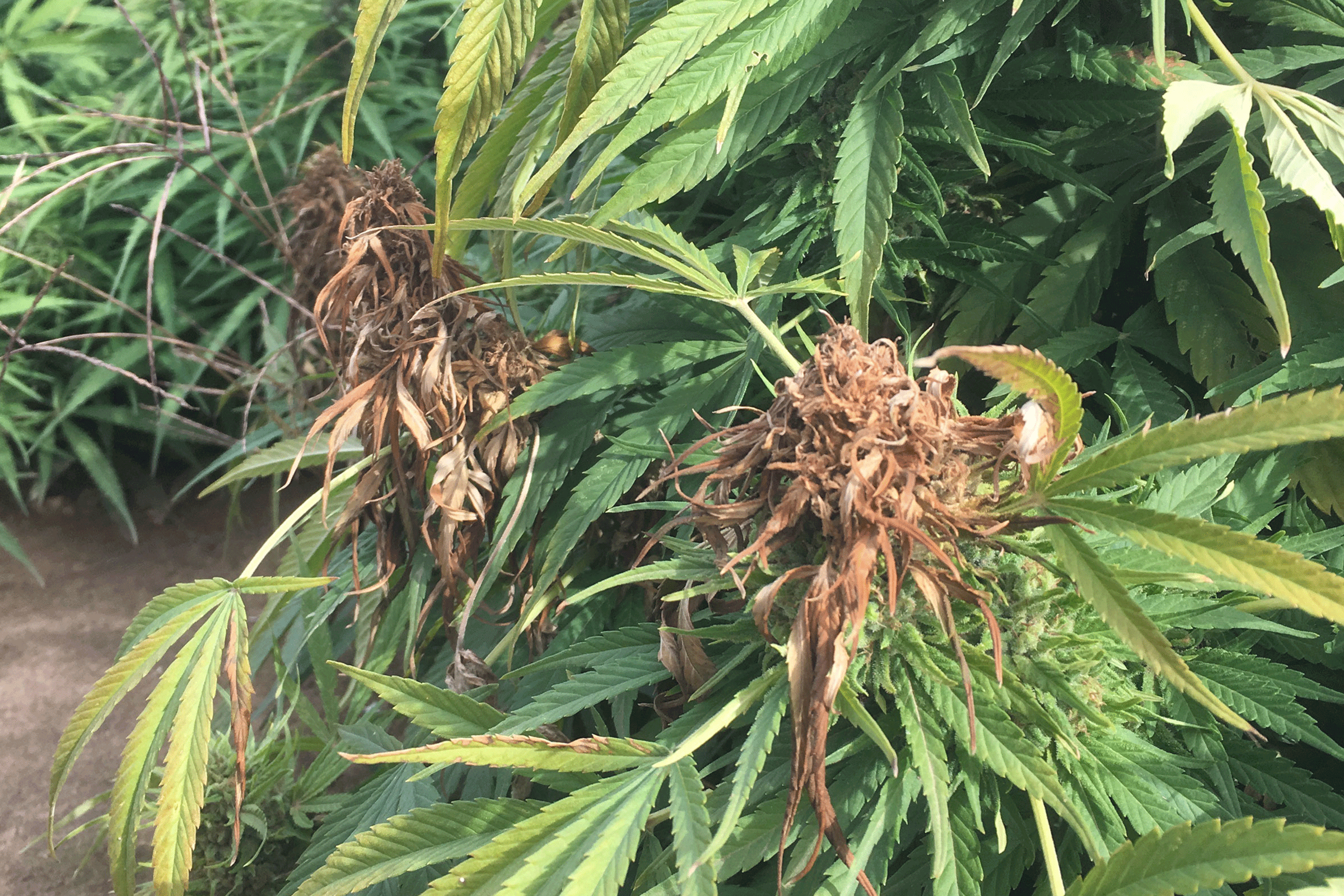
Powdery mildew is the most destructive CBD Hemp pest. It is an obligate pathogen meaning it only lives on the plant and cannot be grown on a culture plate. When it begins, this disease is often invisible to a grower. It tends to emerge, sporulate and spread any time from early vegetative growth phases through flowering, thus destroying very mature crop with severe economic consequences. It is believed to travel in clones, and it is not known if it travels in seeds. It appears as patches of white spores on the surface of leaves, thrives at temperatures between 68° to 77° F and >55% RH, and can cause early leaf drop and reduce flower bud quality.
Botrytis / Gray Mold
Gray mold is caused by Botrytis cinerea, a necrotrophic fungus that can cause severe damage to CBD Hemp and thrives at 68° to 77° F and relative humidity greater than 55%. B. cinerea produces several cell wall-degrading enzymes and toxins that degrade tissues and can also infect plant wounds caused by insects or pruning. The fungus produces gray-white masses of mycelium and spores on the surface of affected tissues.
Gray mold can cause brown, water-soaked lesions on all portions of the plant, including stems, leaves, and especially flowers. Leaves and flowers start to shrivel and turn tan, red or brown as severity increases and masses of gray spores may become evident.
Pythium
The pathogens that are responsible for Pythium root rot, also known as water mold, are present in practically all cultivated soils and attack plant roots under wet conditions. There are many species of Pythium that vary widely. These fungi can be spread by fungus gnats and shore flies, and soil moisture conditions of 70% or higher are conducive to infection by Pythium. Pythium infects juvenile tissues such as the root tip and may spread to the entire primary root, which eventually dies causing the plant to wilt and stop growing.
Sanitation is important because Pythium spp. can survive in dust, planting media, or soil particles on greenhouse floors and in flats and pots. Pythium causes young cuttings and seedlings to wilt even when watered and eventually collapse and die.
Fusarium
Fusarium wilt is caused by two closely related fungi, Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Vasinfectum and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Hemp. Spores are most often found in soil, and can be spread by contaminated water or infected seeds. Once it infects a plant, it travels through the vascular system where the spores and mycelia clog up the xylem, causing the plant to wilt and die from lack of water. Symptoms include leaf yellowing, spots on lower leaves and wilted stems appear brown inside.
Products for Pest Scouting and Monitoring
| Product | What | When | Why |
| Grower’s Edge® Illuminated Magnifier Loupe 40x | Powerful 40x lens with an on/off switch for two LED lights. | Useful at any time of the plant cycle. | Helps to quickly scout for pests. |
| Grower’s Edge® Illuminated Microscope 60x–100x | A very powerful illuminated pocket microscope offering adjustable magnification from 60x–100x. | Useful at any time of the plant cycle. | Ideal for a more in-depth observation of pests. |
| Grower’s Edge® Universal Cell Phone Illuminated Microscope with Clip 60x | This microscope can be clipped onto any smartphone or mobile phone that is equipped with a camera. Images can be taken with your camera and stored in your smartphone’s photo library. | Useful at any time of the plant cycle. | Images can be taken with your camera and stored in your smartphone’s photo library. |
| Grower’s Edge® Aphid Whitefly Sticky Traps | Yellow sticky card traps to monitor flying insects such as fungus gnats, aphids, and whiteflies. | Use during plant growth and flowering. | Yellow traps are more attractive to fungus gnats, aphids, and whiteflies. |
| Grower’s Edge® Thrip and Leafminer Sticky Traps | Blue sticky card traps to monitor flying insects such as thrips and leaf miners. | Use during plant growth and flowering. | Blue traps are more attractive to thrips and leaf miners. |
| Sensor Cards Yellow Monitoring and Trapping Cards | Yellow sticky card traps to monitor flying insects such as fungus gnats, aphids, and whiteflies. | Use during plant growth and flowering. | Yellow traps are more attractive to fungus gnats, aphids, and whiteflies. |

Disclaimer: When using this guide for recommendations on treating plant pest issues, you must always verify and follow any and all product label directions for use as required by federal and state laws.